Trending Content
The US upstream sector began 2024 with $51 billion in mergers and acquisitions though Enverus outlines why the dealmaking may slow down.
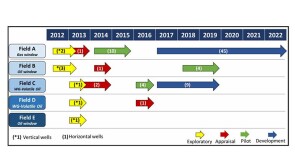
The contracts kick off another round of development in deep and ultradeep water off India’s east coast in the Bay of Bengal.
The supermajor expects its latest development will be online by 2027 and add 250,000 B/D to Guyana's soaring output.
-
If optimized to scale, fast fission reactors could play a role in reducing emissions in field operations by producing carbon-free electricity.
-
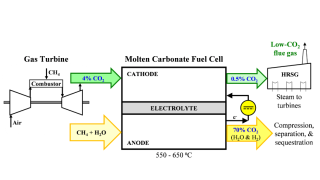
The updated joint development agreement allows the companies to carve out new markets while they complete pilot testing at a demonstration plant in the Netherlands.
-
The project will implement two distinct carbon technologies aimed at capturing and storing carbon dioxide. Svante’s CEO Claude Letourneau describes his company’s solid-sorbent technology used in collaboration with Climeworks, one of the awarded companies.
Get JPT articles in your LinkedIn feed and stay current with oil and gas news and technology.
-
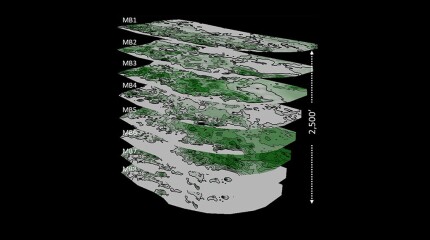
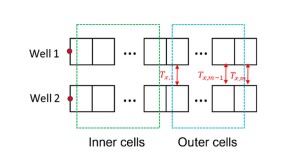
A 44-well development tests what ConocoPhillips has learned about maximizing the value of the wells by figuring out how they drain the reservoir.
-
Jennifer L. Miskimins is the nominee for 2026 SPE President. She and six others make up the new slate of nominees recommended for positions open on the SPE International Board of Directors.
-
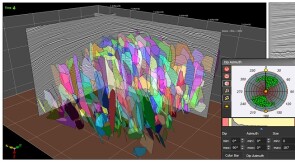
The use of oil-based muds has precluded countless drill cuttings from being used to predict reservoir fluids despite once being part of the reservoir. A 6-decade-old technology may be on the cusp of changing that.
-
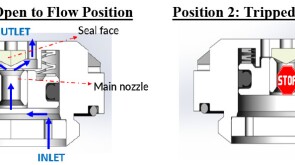
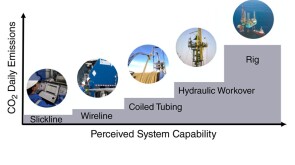
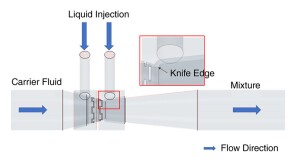
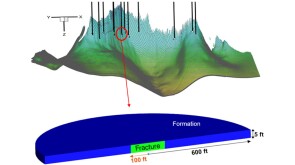
To avoid costly interventions like sidetracking or wellbore abandonment, a check-valve system was installed near the sandface within three injector wells which prevented the mobilization of fines from the reservoir into the wellbore by stopping backflow.
Access to JPT Digital/PDF/Issue
Sign Up for JPT Newsletters
Sign up for the JPT weekly newsletter.
Sign up for the JPT Unconventional Insights monthly newsletter.
President's Column
-
SPE President Terry Palisch is joined by Paige McCown, SPE senior manager of communication and energy education, to discuss how members can improve the industry’s public image.
-
SponsoredExpanding its portfolio of high-tier technologies, TAQA develops a high-performance perforation-plugging patented product.
-
SponsoredWith almost three-quarters of the global greenhouse gas emissions coming from the energy sector, there is a heavy burden and a huge responsibility on the shoulders of all countries of the world to transform the energy sector to be cleaner and greener by eliminating these emissions.
-
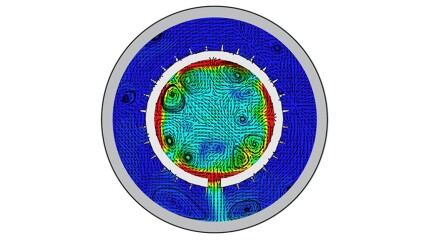
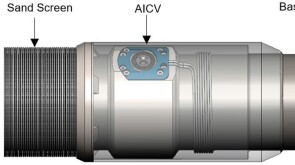
SponsoredSmart completions using autonomous outflow control devices significantly helped in improving reservoir management and increasing oil and gas field productivity by enhancing the injection wells' performance.
-
SponsoredWith more surface facilities and infrastructure in oil and gas fields, well casing integrity is becoming an even bigger challenge. This article sheds light on the optimum way to deal with the increasing casing integrity challenges in the Middle East through field monitoring and time-lapse casing-integrity and corrosion-inspection logging.
Technology Focus
Recommended for You (Login Required for Personalization)
-
Texas has become an early hot spot for geothermal energy exploration as scores of former oil industry workers and executives are taking their knowledge to a new energy source.
-
Ignis H2 Energy and Imeco Inter Sarana announced a strategic partnership to expedite geothermal development in Indonesia.
-
One area where the untapped potential of geothermal energy has been realized is in harnessing thermal energy from abandoned or inactive oil and gas wells. Such wells could be exploited for electricity generation or direct use through well repurposing.
Content by Discipline